The ab unsaturated carbonyl group is a good michael acceptor and undergoes nucleophilic addition. Deketonic form of curcumin deketene curcumin which due to its structure shows greater hydrophilicity than curcumin.
Research Journal Of Pharmaceutical Biological And Chemical Sciences
Curcumin And Natural Derivatives Inhibit Ebola Viral Proteins An In
Curcumin By Donnica Busby On Prezi
A yellow orange dye obtained from tumeric the powdered root of curcuma longa.
Curcumin structure pubchem. Its biological effects range from antioxidant anti inflammatory to inhibition of angiogenesis and is also shown to possess specific antitumoral activity. According to the literature vanilline is the main component in feruloyloacetone synthesis. Curcumin is synthesized by pabons reaction using vanillin and acetyl acetone in the presence of boric oxide.
The diketones form stable enols and are readily deprotonated to form enolates. Curcumin sulfate c21h20o9s cid 66645351 structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities. It is used in the preparation of curcuma paper and the detection of boron.
Curcumin incorporates several functional groups whose structure was first identified in 1910. The aromatic ring systems which are phenols are connected by two ab unsaturated carbonyl groups. Curcumin is a pigment present in curcuma longa l turmeric.
Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2. Curcumin is a biphenolic compound with hydroxyl groups at the ortho position on the two aromatic rings that are connected by a b diketone bridge containing two double bonds dienone which can undergo michael addition critical for some of the effects of curcumin weber et al 2006 but contributing to chemical instability in aqueous solution pan et al 1999. Curcumin appears to possess a spectrum of pharmacological properties due primarily to its inhibitory effects on metabolic enzymes.
Curcumin is a yellow orange dye obtained from tumeric the powdered root of curcuma longa. Curcumin induces senescence of primary human cells building the vasculature in a dna damage and atm independent manner wioleta grabowska karolina kucharewicz maciej wnuk anna lewinska malgorzata suszek dorota przybylska grazyna mosieniak ewa sikora anna bielak zmijewska. This derivative exhibits higher toxicity towards tumor cells than curcumin dahmke boettcher groh mahlknecht 2014.
Curcumin is a natural component of the rhizome of turmeric curcuma longa and one of the most powerful chemopreventive and anticancer agents. Curcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Also called diferuloyl methane it is a symmetric molecule with a seven carbon linker connecting two o methoxy phenolic groups containing aromatic rings.
It is employed in the preparation of curcuma paper the detection of boron and possesses a vast number of biological targets.

Rosocyanine Wikipedia

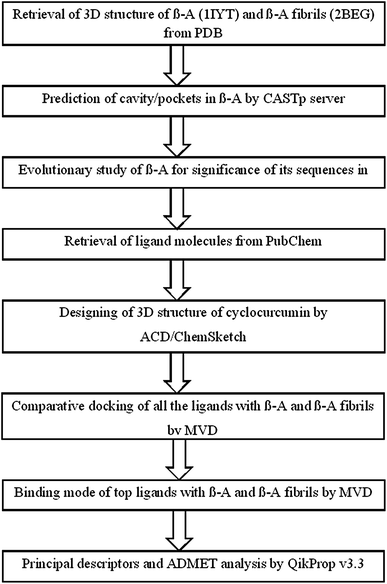
Comparative Docking And Admet Study Of Some Curcumin Derivatives And

Curcumin Ic21h20o6 Pubchem Amyloid Beta Turmeric

EmoticonEmoticon