Researchers believe that decreased levels of acetylcholine in the brain causes alzheimers disease and dementia symptoms. Acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter found in the body and has functions in both the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system.

What Are Cholinesterase Inhibitors And How Do They Function Quora
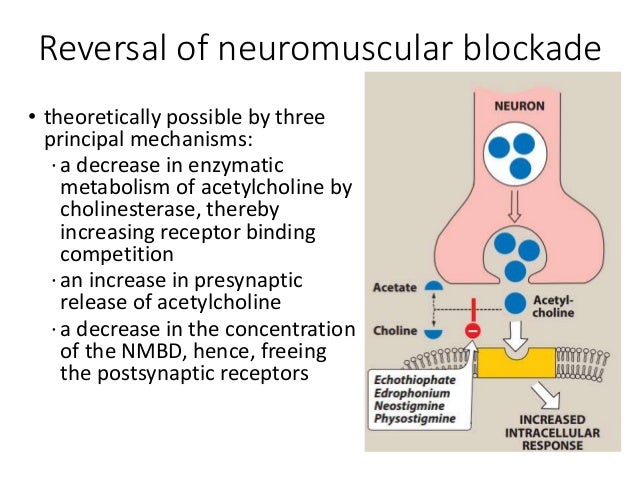
Anticholinesterase Basic Pharmacology And Uses

Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor Wikipedia
Cholinesterase inhibitors acetylchlinesterase inhibitors are medications that block the breakdown acetylcholine a neurotransmitter and that block the action of acetylchlinesterase in the body.

Acetylcholine and cholinesterase. If cholinesterase affecting insecticides are present in the synapses however this situation is thrown out of balance. Cholinesterase ensures that the nervous system works properly by preventing the accumulation of acetylcholine and the overstimulation of muscles and nerves. Cholinesterase breaks apart the neurotransmitter acetylcholine which is vital for the transmission of nerve impulses.
The former are generally have higher toxicity longer duration of action and more. As such cholinesterase inhibitors block the metabolism of acetylcholine. Cholinesterase inhibitors therefore lead to increased levels of acetylcholine and prolonged transmission in cholinergic synapses an action which is mainly used in the treatment of disorders of neuromuscular transmission myasthenia gravis and the antagonism of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockade.
The presence of cholinesterase inhibiting chemicals prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine. In biochemistry a cholinesterase or choline esterase is a family of esterases that lyses choline based esters several of which serve as neurotransmitters. The function of the cholinesterase is to break down a chemical called acetylcholine.
Cholinesterase inhibitors effectively increase the concentration of acetylcholine at all cholinergic. Cholinesterase inhibitors also called acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are a group of medicines that block the normal breakdown of acetylcholine. Cholinesterase inhibitor toxicity is due to a decrease in the ability of cholinesterase to breakdown acetylcholine which results in excessively high acetylcholine levels.
Acetylcholine can then build up causing a jam in the nervous system. Cholinesterase inhibitors are used to reduce the action of cholinesterase thereby making more acetylcholine available to nerve cells in the brain. Cholinesterase inhibitors fall into two classes organophosphorus compounds and carbamates.
Inhibition of acetyl cholinesterase leads to accumulation of acetylcholine at smooth muscle m3 muscarinic receptors and m1m3 muscarinic receptors in salivary glands stomach exocrine pancreas and intestine to produce hypermotility and hypersecretion respectively. The cholinesterase inhibitors increase the activity of cholinergic neurons by blocking the enzyme acetylcholinesterase which metabolizes or breaks down acetylcholine. Thus it is either of two enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of these cholinergic neurotransmitters such as breaking acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid.

Mechanism And Symptoms Of Toxicity And Diagnosis Of Cholinesterase

Figure 2 From Insights Into S Rivastigmine Inhibition Of

Flavonoids As Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Current Therapeutic

EmoticonEmoticon