As a result it changes the state of neuronal networks throughout the brain and modifies their response to internal and external inputs. Acetylcholine is the transmitter of parasympathetic half of the autonomic nervous system.

Cholinergic Drugs
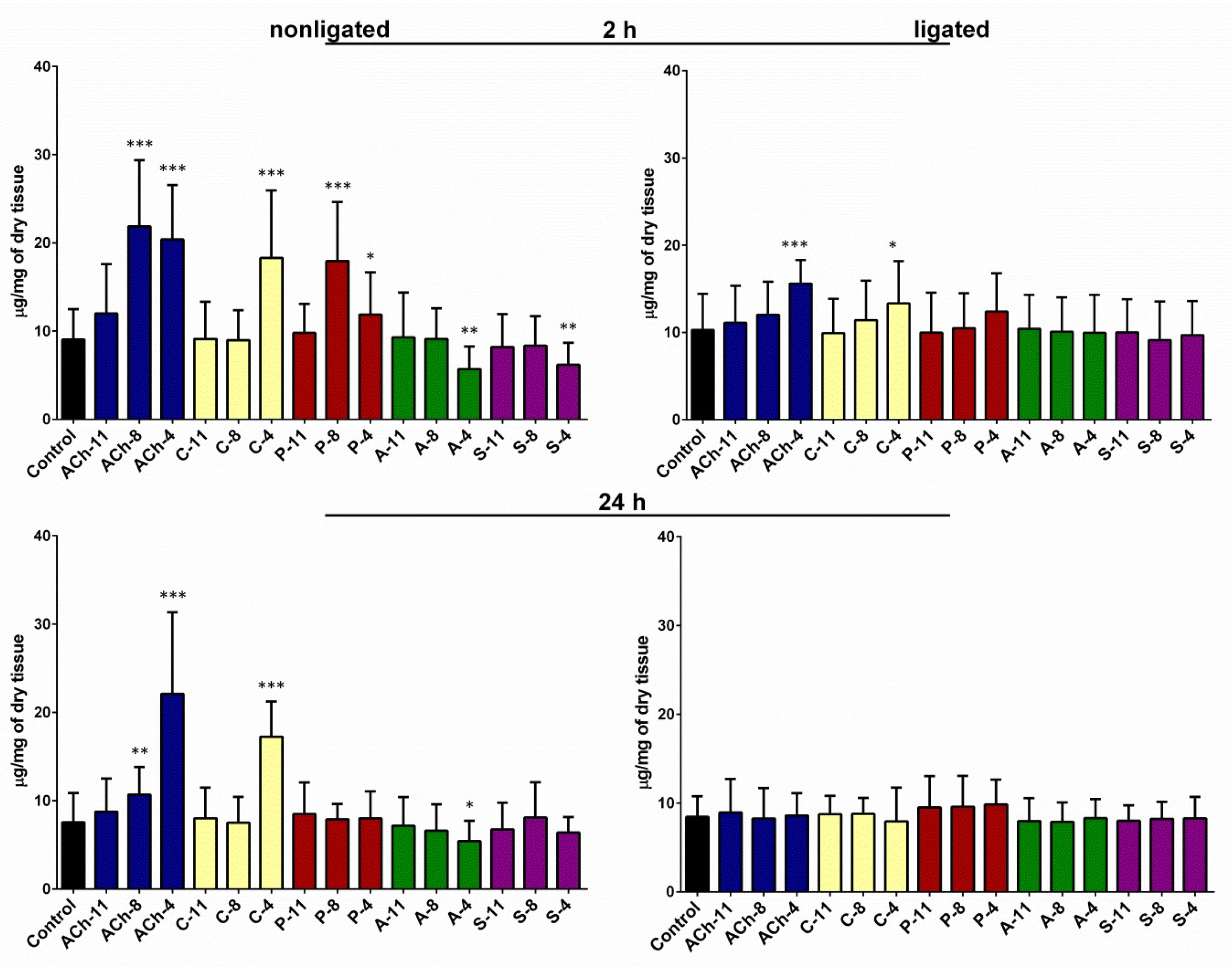
Molecules Free Full Text Cholinergic Agonists And Antagonists
Acetylcholine Receptors Muscarinic And Nicotinic Cme At
This neurotransmitter plays a key role in the functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system along with other aspects of the nervous system.
Acetylcholine cholinergic. When acetylcholine binds to acetylcholine receptors on skeletal muscle fibers it opens ligand gated sodium channels in the cell membrane. Substances that interfere with acetylcholine activity are called anticholinergics. The classical role of a neuromodulator.
One of the primary functions of acetylcholine is to carry signals from motor neurons to the bodys skeletal muscles. In addition the receptor for the merocrine sweat glands are also cholinergic since acetylcholine is released from postganglionic sympathetic neurons. A cholinergic is a substance related to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Many cholinergic drugs are acetylcholine receptor antagonists. Acetylcholine is inactivated by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase which is located at cholinergic synapses and breaks down the acetylcholine molecule into choline and acetate.
Acetylcholine in the brain alters neuronal excitability influences synaptic transmission induces synaptic plasticity and coordinates the firing of groups of neurons. It is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter or a chemical messenger.
Its name is derived from its chemical structure. It does not last long in the bloodstream because it is degraded. Sodium ions then enter the muscle cell initiating a sequence of steps that finally produce muscle.
Acetylcholine has a very short life. Inside the body cholinergic substances regulate parasympathetic activity and serve a number of other functions. It acts at neuromuscular junctions and allows motor neurons to activate muscle action.
Acetylcholine is a transmitter in various brain regions for instance basal ganglia cortex and hypothalamus and is required for proper memory and cognition as well as motor control. In addition to cholinergic agonists and antagonists other drugs can. Acetylcholine is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals and humans as a neurotransmittera chemical message released by nerve cells to send signals to other cells.
It transfers signals between certain cells to affect how your body functions. In the central nervous system acetylcholine and its associated neurons form the cholinergic system. Neuromuscular junctions preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system the basal forebrain and brain stem complexes are also cholinergic.
In the peripheral nervous system acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter that transmits signals between motor nerves and skeletal muscles. One group of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors anticholinesterase drugs is used to treat myasthenia gravis a disorder characterized by muscle weakness. Anticholinergics can treat a variety of conditions including urinary incontinence overactive bladder oab chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder copd and certain types of poisoning.

Neurotransmitters And Receptors Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Top 10 Punto Medio Noticias Cholinergic Postganglionic Sympathetic
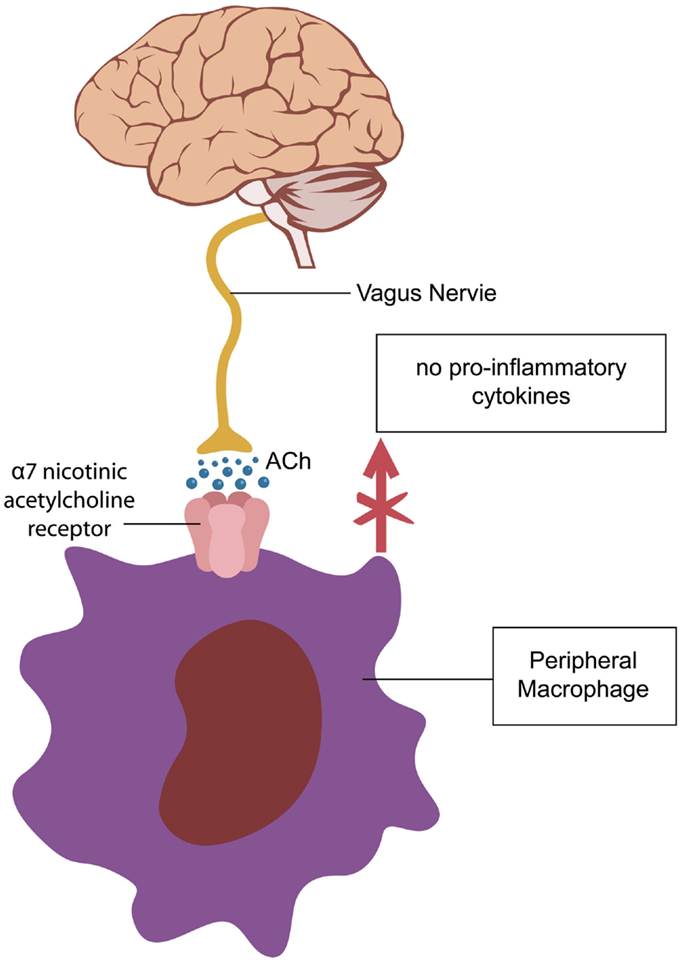
Frontiers Non Neuronal Acetylcholine The Missing Link Between

EmoticonEmoticon