Cholinergic transmission acetylcholine mediated that activates muscarinic receptors occurs mainly at autonomic ganglia organs innervated by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system and in the central nervous system. Nicotinic receptors are the primary mediator of the effects of nicotine.

Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Wikiwand

Acetylcholine Receptor Wikipedia
Biosynthesis Of Acetylcholine In Cns And Cholinergic Transmission
In myasthenia gravis the receptor at the neuromuscular junction is targeted by antibodies leading to muscle weakness.

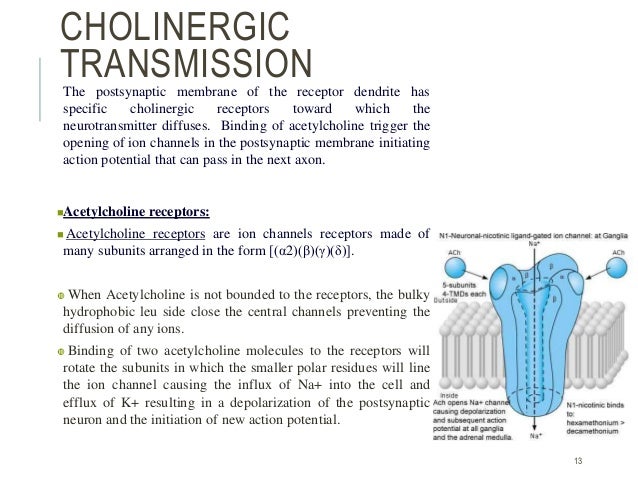
Acetylcholine cholinergic receptors. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the peripheral nervous system are found primarily on autonomic effector cells innervated by postganglionic parasympathetic nerves. The nicotinic achrs are ligand gated ion channels that form pores in cells plasma membranes mediating fast signal transmission at synapses. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are receptors found in the central nervous system the peripheral nervous systems and skeletal muscles.
The cholinergic system in the brain uses the acetylcholine neurotransmitter to communicate. Muscarinic receptors are also present in ganglia and on some cells such as endothelial cells of blood vessels that receive little or no cholinergic innervation. Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter acting on a wide range of functions and tissues throughout the body.
Cholinergic receptors are a certain type of neuron whose molecular structure responds specifically to acetylcholine. There are two types of cholinergic receptors called nicotinic and muscarinic receptors named after the drugs that work on them. A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics in one way or another the action of acetylcholine ach at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors nachrs.
Role in health and disease. Muscarinic acetycholine receptors machr are g protein coupled receptors gpcr that modulate the activity of the cell by activating cellular mechanisms involving second messengers. The autonomic nervous system is one of the major.
Cholinergic receptors are receptors on the surface of cells that get activated when they bind a type of neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. There are five identified types known as m1 to m5. Acetylcholine molecules bind themselves to the receptor molecules on the cells of the receptors.
Nicotinic cholinergic receptors nicotinic receptors are characterised through their interaction with nicotine in tobacco. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors can be blocked by the drugs atropine and scopolamine. Cholinergic receptors are found throughout the nervous system.
Cholinergenic receptors are sensitive to nicotine. The key difference between adrenergic and cholinergic receptors is that the adrenergic receptors are g protein coupled receptors that bind to the neurotransmitters noradrenaline norepinephrine and adrenaline epinephrine while the cholinergic receptors are inotropic and metabotropic receptors that bind to acetylcholine neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine acts by binding to cholinergic receptors the two main types of which are muscarinic and nicotinic.
Nicotine stimulates the part of the autonomic system that reacts to stress factors.

Activation Of The Vagus Nerve Leads To The Release Of Acetylcholine
Metabolism

Signal Transduction Medical Biotechnology Digitalis Tankonyvtar

EmoticonEmoticon