Curcumin can readily transfer electron or easily donate h atom from two phenolic sites to scavenge free radicals. Induces apoptosis in cancer cells and inhibits phorbol ester induced protein kinase c pkc activity.
Black Triangle Png Download 1200 960 Free Transparent Structural

Figure 1 From Structure Activity Relationships Of The Antitumor C5

Simultaneous Quantification Of Free Curcuminoids And Their
The enzyme kinases ikk and gsk3 were thought to be the prime curcumin targets that lead to anti cancer effect but the co crystal structure of curcumin with dyrk2 along with a 140 panel kinase inhibitor profiling reveal that curcumin binds strongly to the active site of dyrk2 inhibiting it at a level that is 500 times more potent than ikk or gsk3.

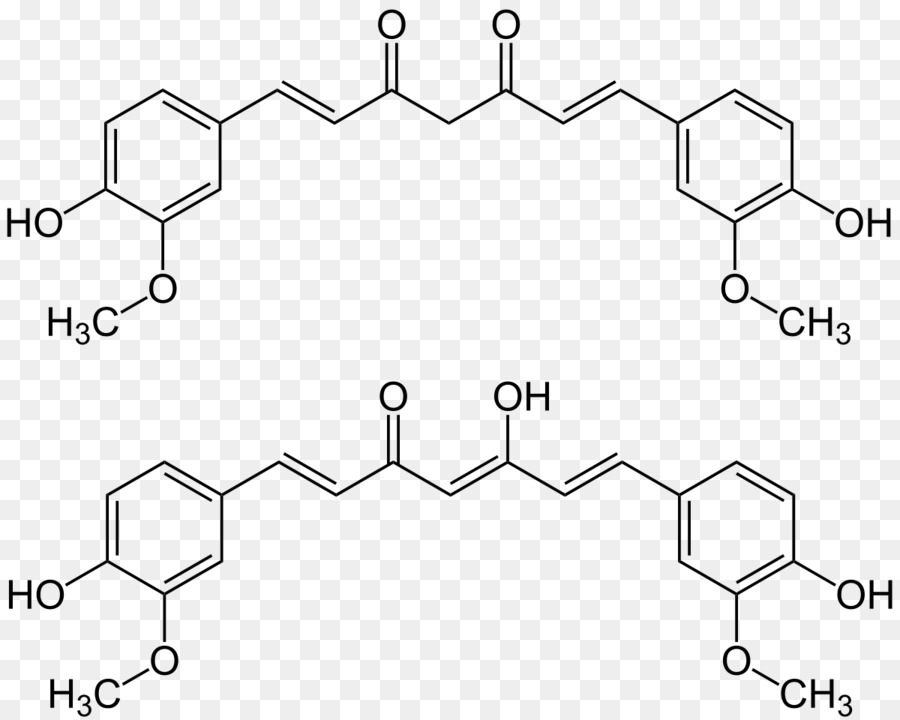
Curcumin structure. In addition curcumin boosts the activity of your bodys own antioxidant enzymes 17 18. Curcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Curcumin is a biphenolic compound with hydroxyl groups at the ortho position on the two aromatic rings that are connected by a b diketone bridge containing two double bonds dienone which can undergo michael addition critical for some of the effects of curcumin weber et al 2006 but contributing to chemical instability in aqueous solution pan et al 1999.
Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2. Curcumin incorporates several functional groups whose structure was first identified in 1910. Curcumin structure function bioavailability and efficacy in models of neuroinflammation and alzheimers disease aynun n.
Lim takashi morihara peter kim. The excellent electron transfer capability of curcumin is because of its unique structure and different functional groups including a beta diketone and several pi electrons that have the capacity to conjugate between two phenyl rings. The aromatic ring systems which are phenols are connected by two ab unsaturated carbonyl groups.
Curcumin is a potent antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals due to its chemical structure 15 16. The ab unsaturated carbonyl group is a good michael acceptor and undergoes nucleophilic addition. Curcumin has been cited as a potential chemopreventive agent in addition to its chemotherapeutic activity.
Curcumin sulfate c21h20o9s cid 66645351 structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities. Potent anti tumor agent having anti inflammatory and anti oxidant properties. The diketones form stable enols and are readily deprotonated to form enolates.
A natural phenolic compound.

Figure 2 From Multiple Biological Actions Of Curcumin In The
File Curcumin Structure Keto Svg Wikimedia Commons
Curcumin Molecular Structure On White Background Stock Photo

EmoticonEmoticon