We will learn more about peptide bonds and how the cleaving process occurs. Thus the newly formed peptide is transferred to the a site and the trna at p site becomes free.
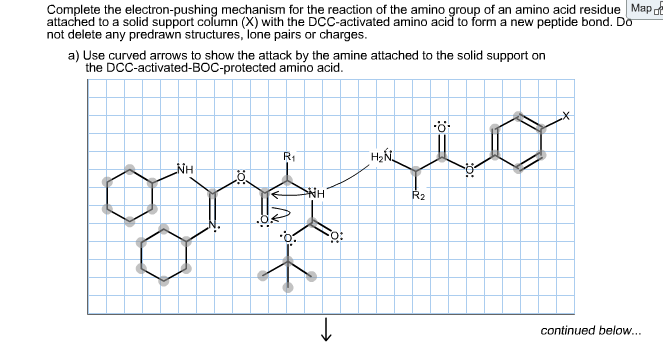
Solved Complete The Electron Pushing Mechanism For The Re
Bioc 212 Protein Folding Bioc 212 Molecular Mechanisms Of Cell
Media Portfolio
Peptide bond formation occurs between the free amino group nh 2 of amino acid attached to trna at a site and carboxyl group by which the initiating amino acid or growing polypeptide chain is attached to the trna at p site.
Amino acid peptide bond mechanism. Created by tracy kim kovach. It can also be called an eupeptide bond to separate it from an isopeptide bond a different type of amide bond between two amino acids. And a very high level overview of this reaction is that this nitrogen uses its lone pair to form a bond with this carbonyl carbon right over here.
Peptide bond formation mechanism a peptide bond forms when the carboxylic acid group r cooh of one amino acid reacts with the amine group r nh 2 of another. Mechanism of peptide bond formation in polypeptide synthesis. That would be the smallest possible peptide but then you could keep adding amino acids and form polypeptides.
Department of biochemistry university of kentucky college of medicine lexington. Grab my free guide for eve. Postdoctoral fellow js and career research awardee rss of the national institutes of health and postdoctoral fellow ra of the american cancer society.
Amino acid peptide linkage and hydrolysis tired of conflicting and confusing mcat advice. It occurs when the carboxylic group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule linking the two molecules and releasing a water molecule. Peptide bonds are formed when the amine group of one amino acid binds with the carbonyl carbon of another amino acid.
The resulting molecule is an amide with a cn bond r co nh r. A dipeptide would have two amino acids. A peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha amino acids from c1 of one alpha amino acid and n2 of another along a peptide or protein chain.
The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds in this case two amino acids.
Proteins

Peptide Bond Formation And Amino Acid Structure Problem

A Molecular Mechanism For The Enzymatic Methylation Of Nitrogen

EmoticonEmoticon