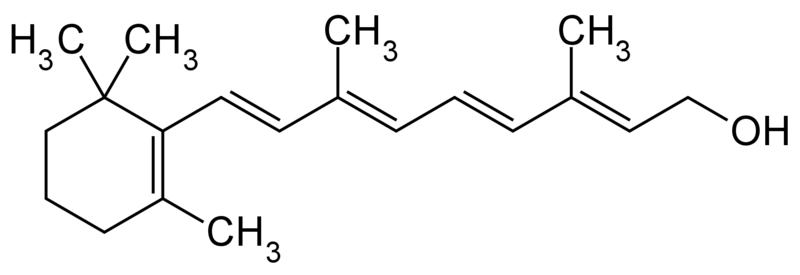
B carotene is the most common form of carotene in plants. The structure was deduced by karrer et al.
Difference Between Vitamin A And Beta Carotene Vitamin A Vs Beta

B Carotene Helps You See In The Dark Crystallography365
Beta Carotene Ymdb01515 Yeast Metabolome Database
When used as a food coloring it has the e number e160a.

Beta carotene structure. In nature b carotene is a precursor inactive form to vitamin a via the action of beta carotene 1515 monooxygenase. Beta carotene is a member of a family of molecules known as the carotenoids. It is broken down in the mucosa of the small intestine by beta carotene dioxygenase to retinal a form of vitamin a.
Beta carotene is a provitamin composed of two retinyl groups. A cyclic carotene obtained by dimerisation of stereoall transstereo retinol. A strongly coloured red orange pigment abundant in plants and fruit and the most active and important provitamin a car otenoid.
Beta carotene is composed of two retinyl groups. Beta carotene is a very strong colored red orange pigment plentiful in various edible plants and fruits. Beta carotene is one of a group of red orange and yellow pigments called carotenoids.
Beta carotene is an antioxidant that can be found in yellow orange and green leafy vegetables and fruits fig. These substances form the coloring pigments for deep yellow orange and dark green fruits and vegetables. These have a basic structure made up of isoprene units.
The presence of long chains of conjugated double bonds donates beta carotene with specific colorst162 it is the most abundant form of carotenoid and it is a precursor of the vitamin a. Beta carotene with the molecular formula c40h56 belongs to the group of carotenoids consisting of isoprene units. What is beta carotene.
Beta carotene and other carotenoids provide approximately 50 of the vitamin a needed in the american diet. Structure of beta carotene beta carotene is one of over 500 of the carotenoid family. It is an organic complex and is chemically categorized as a hydrocarbon and precisely as a terpenoid replicating its derivation from isoprene unitsit is a tetraterpene and a fellow of the carotenes.
Most carotenoids are derived from a 40 carbon basal structure that includes a system of conjugated double bonds 1. These are joined end to end to give a conjugated chain which is common to all carotenoids. The pattern of conjugated double bonds in the carotenoid backbone determines their light absorbing properties and antioxidant ability of carotenoids.

The Chemistry Of Food Colorings American Chemical Society

Beta Carotene Structure C40h56 Over 100 Million Chemical
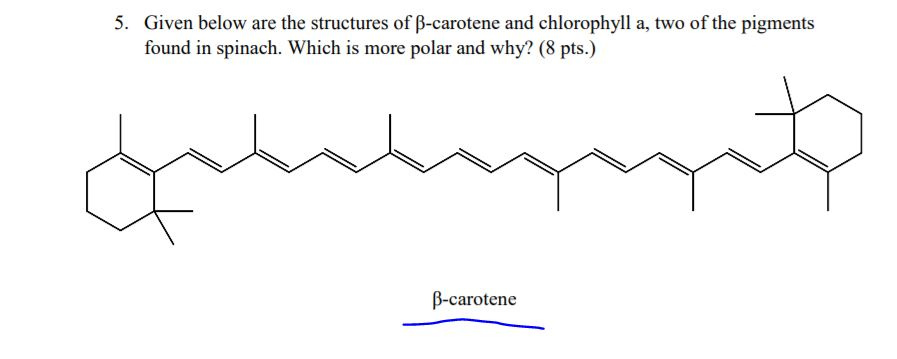
Solved 5 Given Below Are The Structures Of B Carotene An

EmoticonEmoticon