The monomers in a polypeptide are the amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or protein is called the primary structure.

Solved Beginning Within The Nucleus The First Step Leadi

Wo 2017 079723 A1 Targeting Proteins For Degradation The Lens
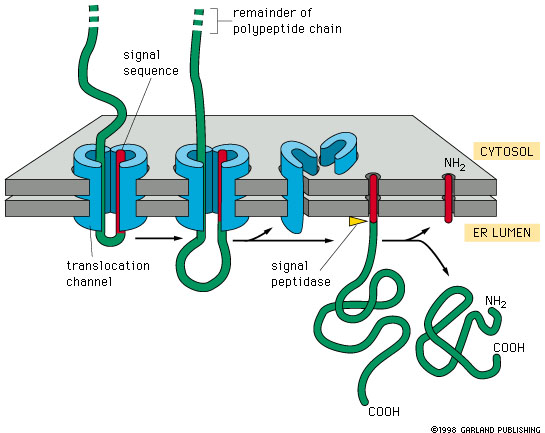
Lecture 27 Protein Targeting Endoplasmic Reticuluum
Protein biosynthesis is most commonly performed by ribosomes in cells.

A polypeptide is a sequence of. By convention the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino terminal end to the carboxyl terminal end. One is to develop a method for making the peptide bond which does not damage anything else in the peptide. Peptides can also be synthesized in the laboratory.
The monomers in a polypeptide are the amino acids. When a sequence has been obtained for a peptide attention can be turned to its synthesis. Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein.
Protein primary structures can be directly sequenced or inferred from dna sequences. The sequence of codons in the mrna was in turn dictated by the sequence of codons in the dna from which the mrna was transcribed. Primary the primary structure of a polypeptide is the linear sequence of its amino acids.
The primary structure of polypeptides and proteins is the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain with reference to the locations of any disulfide bonds. There are two issues to resolve in synthesizing a peptide. If a gene mutation changed one of the amino acids in the sequence the primary structure would change.
Proteins are made up. The term peptide sequence refers to the order in which amino acids are linked. See protein synthesis for details.
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or protein is called the primary structure. Peptides are biological polymers formed by the linking of amino acids the key elements of which are carbon c hydrogen h oxygen o and nitrogen n. The primary structure may be thought of as a complete description of all of the covalent bonding in a polypeptide chain or protein.
Polypeptide chain a sequence of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds forming a protein the sequence being determined by the order of bases along the polynucleotide chains of dna in the form of a genetic code. Peptides are very important in living systems and combine to form much larger chains called proteins. The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide is dictated by the codons in the messenger rna mrna molecules from which the polypeptide was translated.

Sequence Comparison Of The Adrp Like Polypeptide Sequences Of
Peptide Bond Assignment Point

Ch Four Tbs Notes Protein Chem 161 General Biochemistry Studocu

EmoticonEmoticon