Malonyl coa inhibits long chain carnitine acyltransferase activity by all three enzymes at similar concentrations in the physiological range. Carnitine o acetyltransferase also called carnitine acetyltransferase crat or cat ec 2317 is an enzyme that encoded by the crat gene that catalyzes the chemical reaction.
Iii Metabolic Biochemistry Ppt Download

Even Numbered Saturated Fatty Acids

Subcellular Distributions Of Carnitine Acyltransferase Activities
A deficiency of carnitine results in.

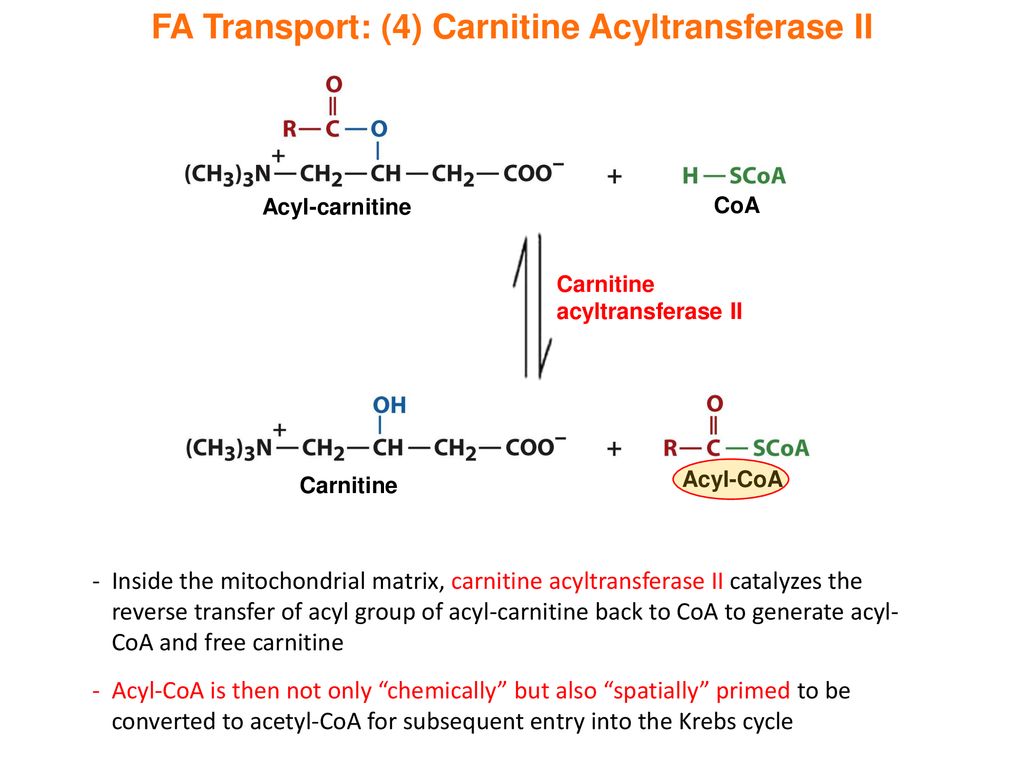
Carnitine acyltransferase. There are three main types of cpt ii deficiency. The acylcarnitine that is formed crosses the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes and then is split in the presence of another form of the enzyme acyltransferase to give carnitine and the acyl molecule which is then oxidized. A lethal neonatal form a severe infantile hepatocardiomuscular form and a myopathic form.
This enzyme catalyzes the reversible transfer of acyl groups from an acyl coa thioester to carnitine and regulates the ratio. Where the acetyl group displaces the hydrogen atom in the central hydroxyl group of carnitine. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase i cpt1 also known as carnitine acyltransferase i cpti cat1 coacarnitine acyl transferase ccat or palmitoylcoa transferase i is a mitochondrial enzyme responsible for the formation of acyl carnitines by catalyzing the transfer of the acyl group of a long chain fatty acyl coa from coenzyme a to l carnitine.
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase ii cpt ii deficiency is a condition that prevents the body from using certain fats for energy particularly during periods without food fasting. Metabolism of fat. Carnitine acyltransferase i appears to be controlled by inhibition by malonyl coa mcgarry et al 1977 and it is logical that when lipogenesis is stimulated the lcfa that are produced should be prevented from entering the mitochondrion where they will be catabolized.
Carnitine acyltransferase i is localized in. Acetyl coa carnitine coa acetylcarnitine. This gene encodes carnitine o acetyltransferase a member of the carnitine acyltransferase family and a key metabolic pathway enzyme which plays an important role in energy homeostasis and fat metabolism.
Carnitine b hydroxy g n trimethylaminobutyric acid 3 hydroxy 4 nnn trimethylaminobutyrate is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals plants and some bacteria. Carnitine may exist in two isomers labeled d carnitine and l carnitine as they are optically active. Fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism.
Fatty acids are transported across. The transfer of acylcoa into the mitochondrial matrix occurs through the agency. One of the most common regulation systems of carnitine acyltransferases involves inhibition by malonyl coa an intermediate in the synthesis of fatty acids.
A cytosol b inner mitochondrial membrane c outer mitochondrial membrane. Excessive long medium or short chain acyl coas.

In The Mitochondria Carnitine Acyltransferase Ii Transfers The Fatty

Crot Research Products Novus Biologicals
1 Introduction To Lipid Metabolism Roles Of Lipids Lipids Have A

EmoticonEmoticon