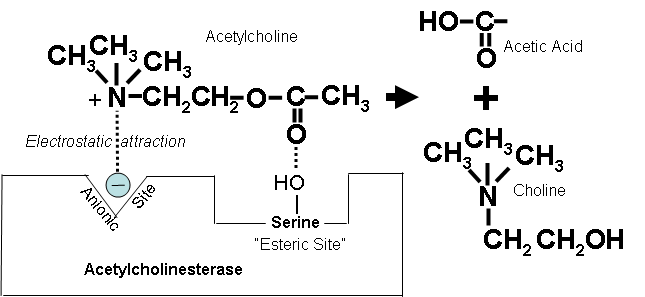
Acetylcholine transmitter substance of nerve impulses within the central and peripheral nervous systems. The esteratic subsite where acetylcholine is hydrolyzed to acetate and choline contains the catalytic triad of three amino acids.

Acetylcholine Chloride Pkg Of 150 Mg Per Vial Sigma Aldrich

Probing The Structure Of The Uncoupled Nicotinic Acetylcholine

Exe
Molecular formula c 7 h 16 no 2.

Acetylcholine structure. Acetylcholine while inducing contraction of skeletal muscles instead induces decreased contraction in cardiac muscle fibers. These three amino acids are similar to the triad in other serine proteases except that the glutamate is. Monoisotopic mass 146117554 da.
Acetylcholine is a cholinergic receptor agonist. However a lack of structural information for this receptor subtype has limited further drug development and validation. It is the chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system which contracts smooth muscles dilates blood vessels increases bodily secretions and slows heart rate.
Acetylcholine is the transmitter of parasympathetic half of the autonomic nervous system. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter produced by neurons referred to as cholinergic neurons. Enzyme structure and mechanism.
Acetylcholine is a transmitter in various brain regions for instance basal ganglia cortex and hypothalamus and is required for proper memory and cognition as well as motor control. This distinction is attributed to differences in receptor structure between skeletal and cardiac fibers. In the peripheral nervous system acetylcholine plays a role in skeletal muscle movement as well as in the regulation of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle.
Average mass 146207 da. Serine 200 histidine 440 and glutamate 327. The human m5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor machr has recently emerged as an exciting therapeutic target for treating a range of disorders including drug addiction.
It is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Its name is derived from its chemical structure. The mechanism of action of acetylcholine is as a cholinergic agonist.
Acetylcholine ach is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals and humans as a neurotransmittera chemical message released by nerve cells to send signals to other cells neurons muscle cells and gland cells. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter found at neuromuscular junctions autonomic ganglia parasympathetic effector junctions a subset of sympathetic effector junctions and at many sites in the central nervous system. In the central nervous system acetylcholine is believed to be involved in learning memory and mood.
Sodium ions then enter the muscle cell stimulating muscle contraction.
Cholinesterase Inhibitors What Are Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Diversity Of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Positive Allosteric

Chemical Structure Of Dmae A Choline B And Acetylcholine C

EmoticonEmoticon