Mechanism of action acetylcholine is a direct acting parasympathomimetic ophthalmic agent used to produce miosis during ophthalmic surgery. Acetylcholine is used by bacteria fungi and a variety of other animals.

Neurotransmitters And Its Mechanism Of Action

Cholinergic Blocking Drugs Nurse Key
Cholinergic Pharmacology Basicmedical Key
Nicotinic receptors mediate their responses by opening a.
Acetylcholine drug mechanism of action. Acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter responsible for neurotransmission at. Cholinergic drugs work with the parasympathetic nervous system. The cholinergic drugs which are described in this and the following chapter act on receptors that are activated by acetylcholine.
Cholinergic drugs are used as substitutes. Acetylcholine is a cholinergic receptor agonist. The second group act on receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine.
Many of the uses of acetylcholine rely on its action on ion channels via gpcrs like membrane proteins3. Acetylcholine ach is a neurotransmitter. The parasympathetic nervous system.
Casey is a 90 year old woman who has recently been diagnosed. Knowledge of ache structure is essential for understanding its high catalytic efficacy and the molecular basis for the recognition of ach by other ach binding protein ach receptors as well as elucidation of the mechanism of action underlying the pharmacological and toxicological action of these agents for the purpose of rational drug design. Mechanism of action when to use cholinergic drugs.
The mechanism of action of acetylcholine is as a cholinergic agonist. Cholinergic and adrenergic drugs both act by either stimulating or blocking receptors of the autonomic nervous system. The two major types of acetylcholine receptors muscarinic and nicotinic receptors have convergently evolved to be responsive to acetylcholine.
It is a naturally occurring neurohormone that helps transmit nerve impulses at all cholinergic sites including somatic and autonomic nerves. Acetylcholine in vertebrates is the major transmitter at neuromuscular junctions autonomic ganglia parasympathetic effector junctions. Muscarinic receptors mediate their responses by g proteins.
Function and mechanism of action the acetylcholine is the specific neurotransmitter in the systems of the somatic nervous system and the ganglionic synapses of the autonomic nervous system. The endogenous agonist for muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.
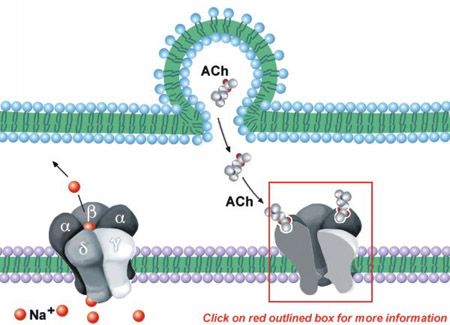
Acetylcholine Neurotransmission Section 1 Chapter 11 Neuroscience
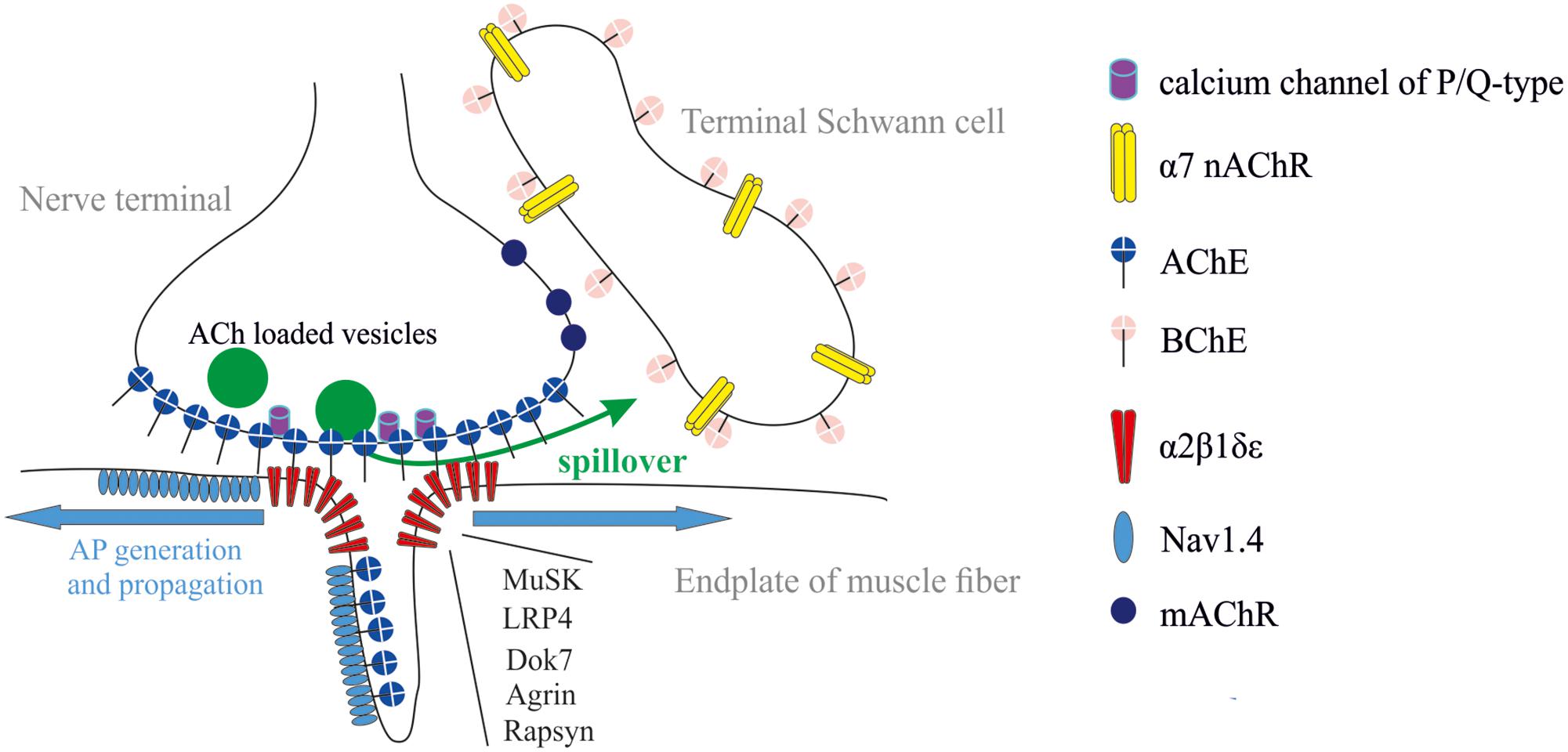
Frontiers Autoregulation Of Acetylcholine Release And Micro

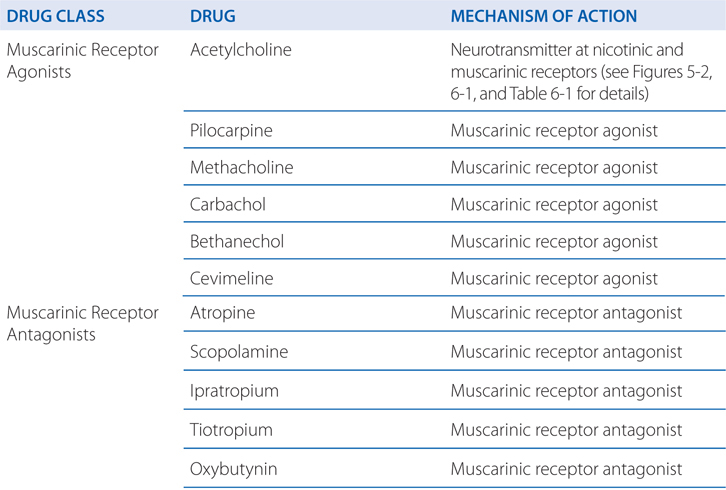
Solved 5 Acetylcholinesterase Which Breaks Down Acetylc

EmoticonEmoticon