Carnitine biosynthesis and regulation of tissue carnitine content. L carnitine is an endogenous molecule involved in fatty acid metabolism biosynthesized within the human body using amino acids.
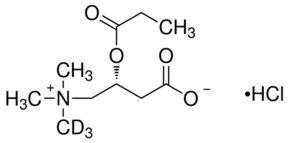
Propionyl L Carnitine N Methyl D3 Hydrochloride 99 Atom D 98
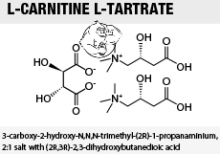
Acetyl L Carnitine L Tartrate In N2guard Evolutionary Org
Carnitine Molecule Chemical Structure Stock Photo Thinkstock
L carnitine transports activated long chain fas from the cytosol into the mitochondrion and is therefore essential for fao.

Carnitine structure. It is most accumulated in cardiac and skeletal muscles as it accounts for 01 of its dry matter. L lysine and l methionine as substrates. In supplement form its available as a capsule liquid or even injectable.
In the body acetyl l carnitine is made from l carnitine. Structure properties spectra suppliers and links for. Carnitine occurs in two forms or isomers.
Those with genetic disorders disease vegetarians underweight. L carnitine is the active form that plays a role in energy metabolism and production. Carnitine is a constituent of striated muscle and liver.
Carnitine helps turn body fat into energy. Carnitine is the generic expression for a number of compounds that include l carnitine acetyl l carnitine and propionyl l carnitine. L carnitine is an amino acid a building block for proteins that is naturally produced in the body.
Carnitine is produced by the liver and kidneys and stored in skeletal brain and heart tissue that use fatty acids as energy r. Carnitine is an amino acid derivative. It is used therapeutically to stimulate gastric and pancreatic secretions and in the treatment of hyperlipoproteinemiastarget.
It also gets rid of toxic compounds from the mitochondria to prevent build up. To guarantee continuous energy supply the human body oxidizes considerable amounts of fat besides glucose. It is produced within the body but it can also be taken as a supplement or found in many different protein foods as well.
Carnitine metabolism was studied in the fetal placental unit by measuring carnitine metabolites intermediary metabolites of carnitine biosynthesis as well as the activity of carnitine biosynthesis enzymes in human term placenta cord blood and selected embryonic and fetal tissues 5 20 weeks of development. It can also be converted to l carnitine. It is an amino acid derivative and an essential cofactor for fatty acid metabolism.
Carnitine facilitates long chain fatty acid entry into mitochondria delivering substrate for oxidation and subsequent energy production. L carnitine is constituent of striated muscle and liver. Carnitine derived from an amino acid is found in nearly all organisms and animal tissue.

L Carnitine Tartrate

Doctor S Best L Carnitine Fumarate Non Gmo Vegan Gluten Free Heart Health 855 Mg 60

File Carnitine 3d Structure Png Wikimedia Commons

EmoticonEmoticon