Enzymes are made up of proteins. Amino acyl trna binds to the a site peptidyl transferase cleaves the amino acid from the p site trna it bonds it to the amino acid on the a site trna ribosome moves along the mrna to the next codon the trna with the polypeptide chain is brought to the p site the empty trna is moved to the e site the ribosome moves over one codon the empty.

Chymotrypsin Wikipedia

Fluorogenic Peptide Substrate For Quantification Of Bacterial Enzyme
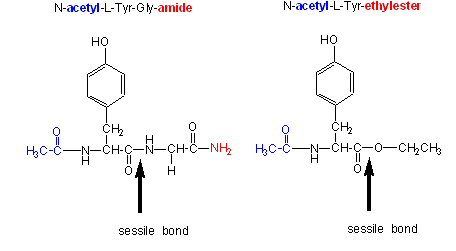
B3 Chymotrypsin Biology Libretexts
It is converted into a fully active enzyme when the peptide bond joining arginine 15 and isoleucine 16 is cleaved by trypsin figure 1032.

A polypeptide is cleaved by an enzyme making it active. When you purify enzyme e you obtain a single type of polypeptide of 50 kd. A enzyme e is the product of gene g that encodes a protein with the molecular weight of 50 kilodaltons 50 kd. In other cases as will be mentioned below mrna carries a transcript of several genes resulting in the synthesis of a large polypeptide that must subsequently be cleaved by enzymes called.
Conformational changes in the enzymes between tense form less active and relaxed form more active allows cooperative binding and associated kinetic modulation depends on whether you have different subunits of the enzyme is it going to act as a dimer tetramer etc. Chymotrypsinogen a single polypeptide chain consisting of 245 amino acid residues is virtually devoid of enzymatic activity. The first processing is the n terminal signal peptide cleavage to produce the proenzyme ie.
The resulting active enzyme called p chymotrypsin then acts on other p chymotrypsin molecules. However active enzyme e has a molecular weight of 250 kilodaltons 250 kd not 50 kd. Proteolytic activation is the activation of an enzyme by peptide cleavage.
Irreversible conversions can occur on inactive enzymes to become active. The enzyme is initially transcribed in a longer inactive form. Can either change binding efficiency or enzymatic activity.
In this enzyme regulation process the enzyme is shifted between the inactive and active state. An inactive form of an enzyme that must have part of its polypeptide chain cleaved before it becomes active allosterism a type of enzyme regulation based on an event occurring on the enzyme at a place other than the active site but that creates a change in the active site. At a high temperature the polypeptide chains of the enzyme are unfolded hence it loses its specific 3d configuration and active site and is denatured.
The enzyme is biosynthesized as a preproprotein which is converted to the active enzyme through proteolytic processing at four sites.

Catalytic Triad Wikipedia
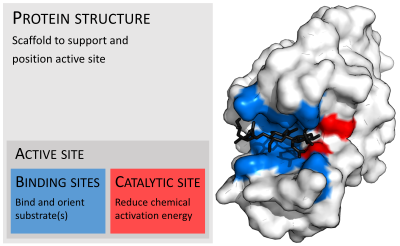
Active Site Wikipedia

Enzyme Definition Mechanisms Nomenclature Britannica Com

EmoticonEmoticon