This article needs more medical references for. The intracellular routing of choline to its various metabolic pathways phosphorylation oxidation and acetylation is cell and tissue specific.
Nutrients Free Full Text Common Genetic Variants Alter

Choline Kinase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Figure 1 From Radioactive Choline Metabolism In Guinea Pig
Choline is an essential water soluble nutrient that is usually grouped in as part of the b vitamin complex.
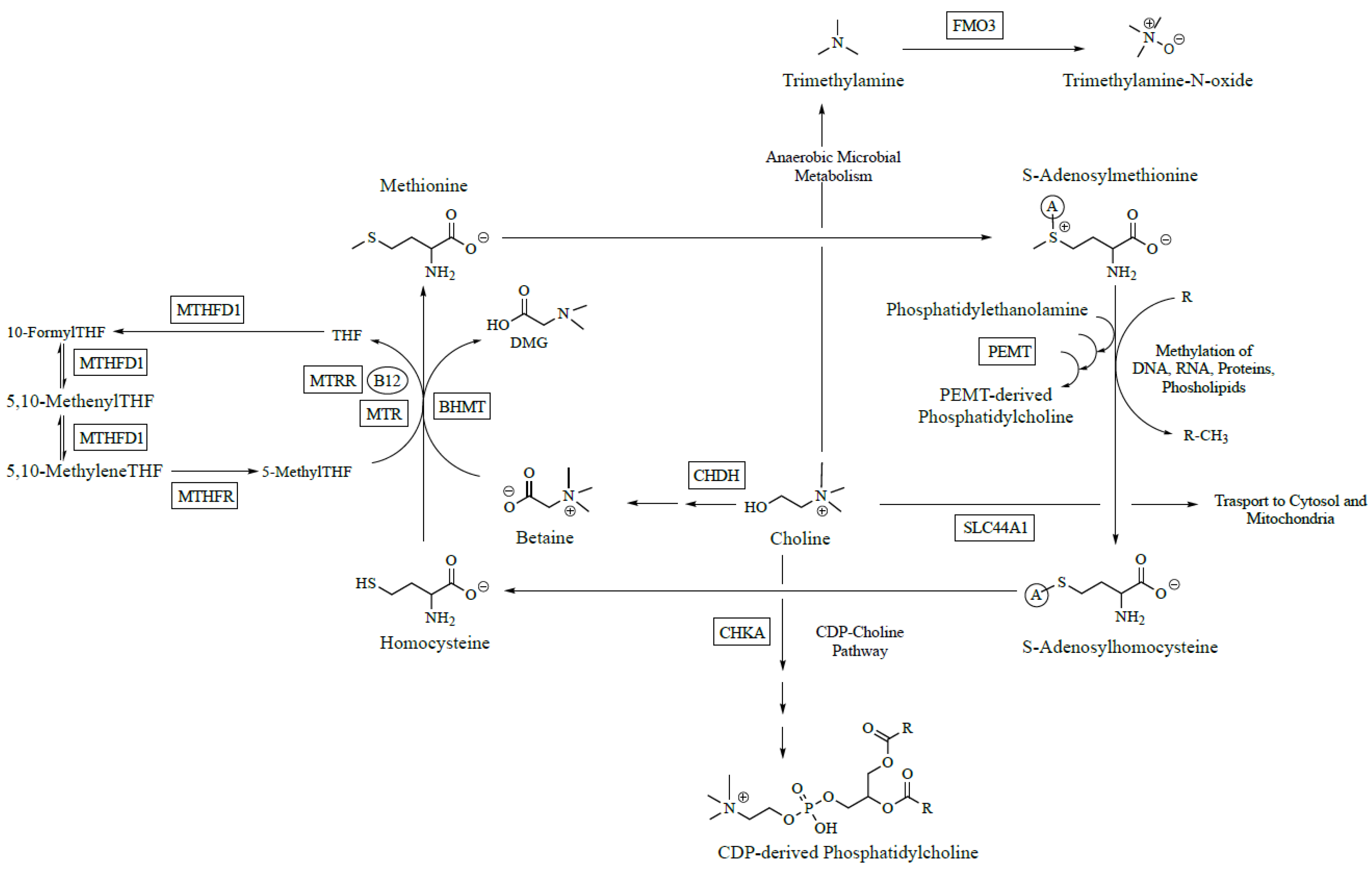
Choline metabolism. Although not technically a vitamin by strict definition this organic compound is required for lifes most quintessential functions including basic cellular structure nutrient transport and metabolism. Choline is an essential nutrient and the liver is a central organ responsible for choline metabolism. Jump to navigation jump to search.
The body needs choline to synthesize phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin two major phospholipids vital for cell membranes. Choline is an essential nutrient that is naturally present in some foods and available as a dietary supplement. Choline is a vitamin like essential nutrient and a methyl donor involved in many physiological processes including normal metabolism and transport of lipids methylation reactions and neurotransmitter synthesis.
Choline is an organic water soluble compound. We found that toll like receptor tlr activation enhances choline uptake by macrophages and microglia through induction of the choline transporter ctl1. Choline is present in the form of phosphatidycholine a compound that makes up the structural component of fat and thus can be found in different types of foods that naturally contain certain fats.
This means its required for normal bodily function and human health. Although small amounts of it can be made in the liver the majority must be obtained from the diet. Choline is a macronutrient thats important for liver function normal brain development nerve function muscle movement supporting energy levels and maintaining a healthy metabolism.
Choline is a source of methyl groups needed for many steps in metabolism. It is classified as neither a vitamin nor a mineral. Choline metabolism choline is the precursor of various metabolites.
Choline is an essential nutrient 2. In the last few years there have been significant advances in our understanding of the mechanisms that influence choline requirements in humans and in our understanding of cholines effects on liver function. Hepatosteatosis and liver cell death occur when humans are deprived of choline.
Choline is a vitamin like nutrient that is taken up via specific transporters and metabolized by choline kinase which converts it to phosphocholine needed for de novo synthesis of phosphatidylcholine pc the main phospholipid of cellular membranes.

Figure 1 From Comparative Genomics And Mutagenesis Analyses Of
Choline Metabolism In Discrete Areas Of The Brain The Effect Of
Changes In Gene Transcription Underlying The Aberrant Citrate And

EmoticonEmoticon