Amino acid is a small molecule that contains an amino group nh 2 and a carboxylic acid group cooh which are bound to a central carbon atom with an additional hydrogen and a side chain r group. This sequence ultimately determines the shape that the protein adopts according to the spatial limitations on the arrangement of the atoms in the protein the chemical properties of the component amino acid residues and the proteins.
Protein Structure

12 Proteins Amino Acids Peptid Bonds Biology Notes For A Level
Chapter 5 Amino Acids And Peptides
It can also be called an eupeptide bond to separate it from an isopeptide bond a different type of amide bond between two amino acids.
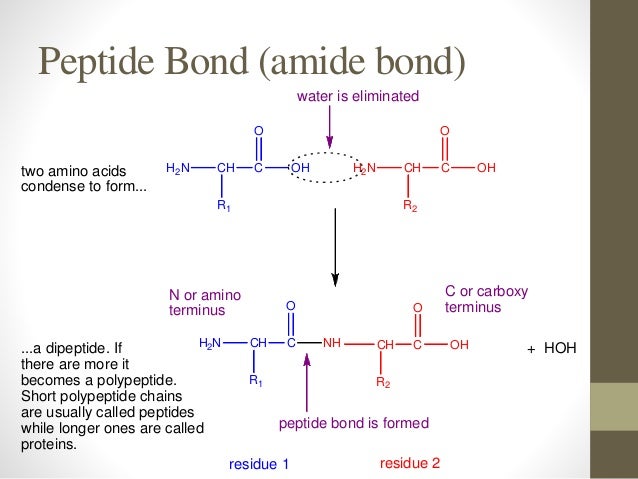
Amino acid peptide bond protein. The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds in this case two amino acids. 12 the peptide bond and primary structure of proteins. Peptide bond sometimes called a peptide.
A fourth bond attaches a carbon to a side group that varies among different amino acids. And then we have the release of a water molecule. And so you have this oxygen is this oxygen and you could imagine that this hydrogen is this hydrogen and this hydrogen is this hydrogen right over here and so net net it all works out.
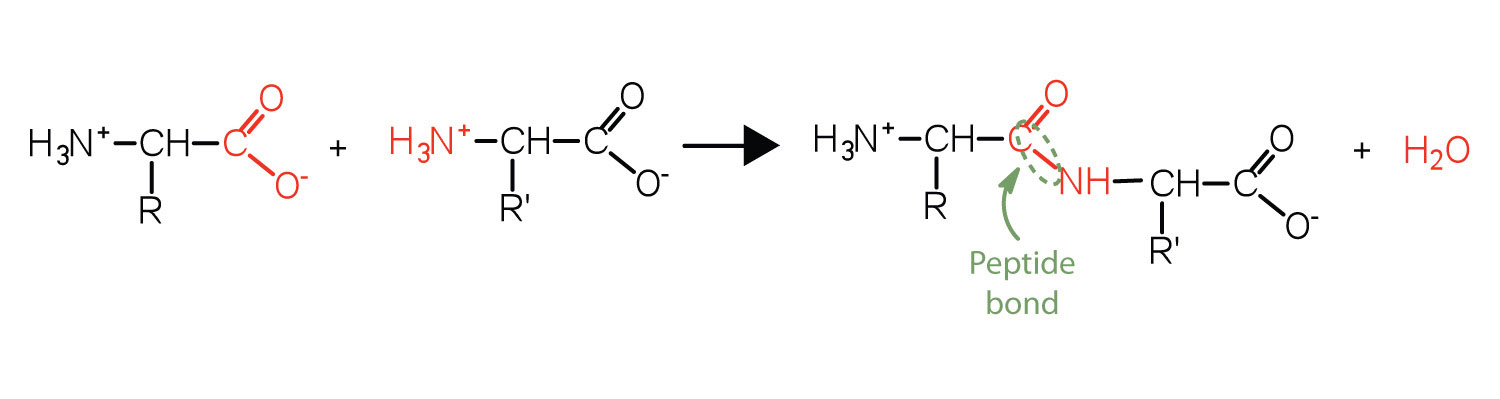
A peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha amino acids from c1 of one alpha amino acid and n2 of another along a peptide or protein chain. These side groups are important as they affect the way a proteins amino acids interact with one another and how a protein interacts with other molecules. The primary structure of a protein is defined as the sequence of amino acids of which it is composed.
Amino acids are the building blocks of both peptides and proteins. All attached to same carbon atom the acarbon or alpha carbon. It occurs when the carboxylic group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule linking the two molecules and releasing a water molecule.
Difference between peptide and protein. The peptide is formed between the amino group nh2 of the first amino acid and carboxyl group cooh of the second amino acid by eliminating one molecule of water the amino acids are held together in a protein by covalent peptide bonds or linkages.
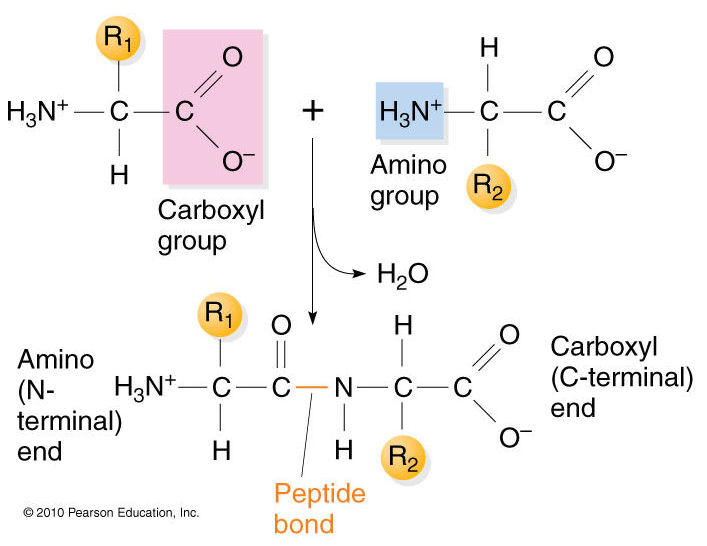
Peptide Bond Formation

Peptides
Does A Peptide Bond Form Between The Functional R Groups Of Amino

EmoticonEmoticon