What are peptide bonds. Two amino acid molecules can be covalently joined through a substituted amide linkage termed a peptide bond to yield a dipeptide.
Plant And Soil Sciences Elibrary

Figure 2 From Formation Of Oligopeptides In High Yield Under Simple
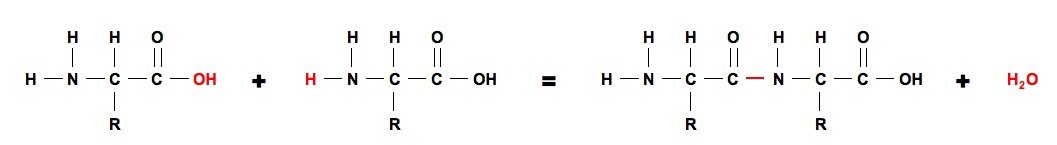
Peptide Bonds Bioninja
The loss of a water molecule occurs during formation of the peptide bond and the basic amino acid unit in a protein chain is therefore referred to as an amino acid residue.
Amino acid peptide bond formation. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between two amino acids. A peptide bond is the amide bond which is formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid becomes linked to the amino group of another to form a peptide. Furthermore among the 22 proteinogenic amino acids 9 of them are identified as essential amino acids as they cannot be synthesised by the human body with the use of other compounds.
It occurs when the carboxylic group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule linking the two molecules and releasing a water molecule. Amino acid peptide bonds. The loss of a water molecule occurs during formation of the peptide bond and the basic amino acid unit in a protein chain is therefore referred to as an amino acid residue.
The acid group of the first is close to the amine group of the second. Long chain polypeptides can be formed by linking many amino acids to each other via peptide bonds. A dipeptide would have two amino acids.
The peptide bond is left between the two amino acids. Next a water molecule is eliminated leaving a bond between the acid carbon of the first amino acid and the amine nitrogen of the second. That would be the smallest possible peptide but then you could keep adding amino acids and form polypeptides.
Proteins are used in many roles including structural support catalyzing important reactions and recognizing molecules in the environment. If the order of listing the amino acids is reversed a different dipeptide is formed such as alaninylglycine. First two amino acids are brought together.
Formation of peptide bonds. Such a linkage is formed by removal of the elements of water from the a carboxyl group of one amino acid and the a amino group of another fig. Living organisms use peptide bonds to form long chains of amino acids known as proteins.
And a very high level overview of this reaction is that this nitrogen uses its lone pair to form a bond with this carbonyl carbon right over here. As mentioned above a peptide bond is the main reaction between amino acids in the formation of proteins. A peptide bond is the amide bond which is formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid becomes linked to the amino group of another to form a peptide.
The carboxyl oxygen green and the amine nitrogen green join to form the amide bond. How amino acids including ones in zwitterion form form peptide bonds peptide linkages through a condensation reaction dehydration synthesis. The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds in this case two amino acids.
Oxygen red from the acid and hydrogens red on the amine form a water molecule.

Chemistry Of Amino Acids And Protein Structure Article Khan Academy
How Is A Peptide Bond Formed

Biochemistry Lecture 3 Bcmb20002 Biochemistry And Molecular

EmoticonEmoticon