The most common types of disaccharidessucrose lactose and maltosehave 12 carbon atoms with the general formula c12h22o11. Glucose is a monosaccharide and reducing sugar which is the main product of photosynthesis in plants.
Pdb 101 Global Health Diabetes Mellitus Drugs Alpha Glucosidase

2 1 Essential Ideas
Intro Bio Lec 2 Columbia University
When a compound with beta confirmation links with another compound with beta confirmation the linkage is beta linkage.

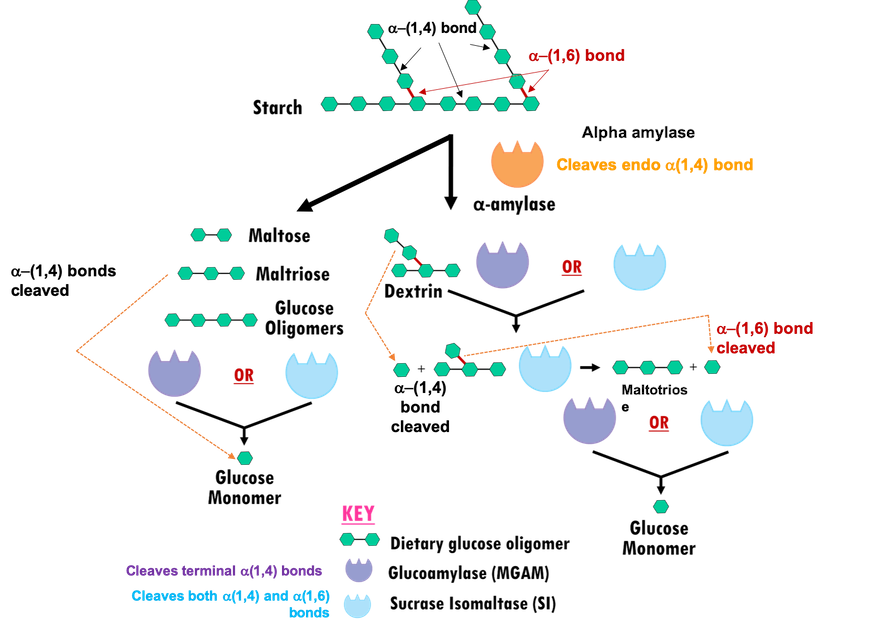
Alpha glucose linkage. Section 112complex carbohydrates are formed by linkage of monosaccharides. Three common examples are sucrose lactose and maltose. Example maltose alpha d glucose linked to another alpha d glucose with alpha 1 4 linkage 2.
No cable box required. In maltose for example two d glucose residues are joined by a glycosidic linkage between the a anomeric form of c 1 on one sugar and the hydroxyl oxygen atom on c 4 of the adjacent sugar. A substance containing a glycosidic bond is a glycoside.
1when a compound with alpha confirmation links with another compound with alpha confirmation the linkage is alpha linkage. The differences in these disaccharides are due to atomic arrangements within the. As a result of the bond angles in the beta acetal linkage cellulose is mostly a.
The term glycoside is now extended to also cover compounds with bonds formed between hemiacetal groups of sugars and several chemical groups other than hydroxyls such as sr ser nr1r2 or even cr1r2r3. Like monosaccharides disaccharides are soluble in water. Disaccharides are one of the four chemical groupings of carbohydrates.
The future of live tv with 70 channels. Particularly in naturally occurring glycosides the compound roh from which the carbohy. Amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide joined by alpha 14 linkages with branch points of alpha 16.
Chlorophylls produce glucose and oxygen using inorganic carbon and water. Such a linkage is called an a 14 glycosidic bond. A glucose vs b glucose vs linear glucose.
Alpha glucose is the monomer unit in. A disaccharide is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage. When two alpha d glucose molecules join together a more commonly occurring isomer of glucose compared to the l glucose form a glycosidic linkage the term is known as a a 14 glycosidic bond.
So sunlight is fixed into chemical energy through glucose. Alpha vs beta glucose glucose is the unit of carbohydrate and show the unique characteristic of the carbohydrate. Beta glucose is the monomer unit in cellulose.
The 1 4 linkage is because c1 of one glucose molecule is linked to the c4 of the next. As a result of the bond angles in the alpha acetal linkage starch amylose actually forms a spiral structure. A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide and the hydroxyl group of some compound such as an alcohol.
Food Chemistry
What Is The Name Of The Linkage Connecting Monosaccharide Units In

Glycosidic Bond An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

EmoticonEmoticon