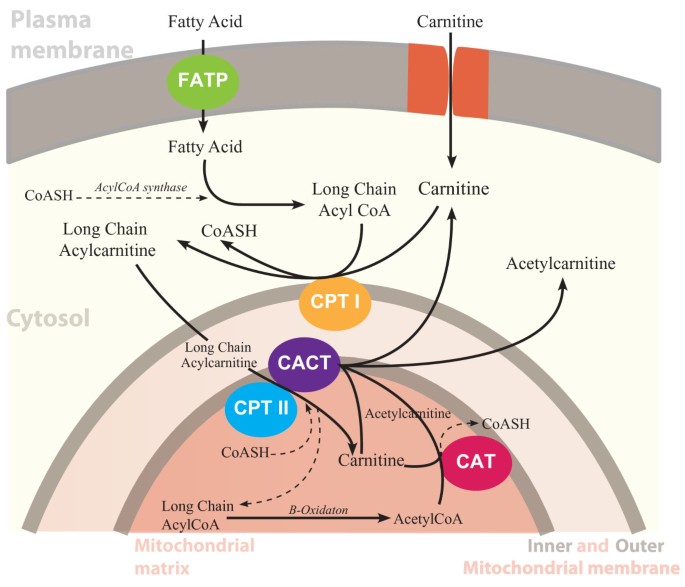
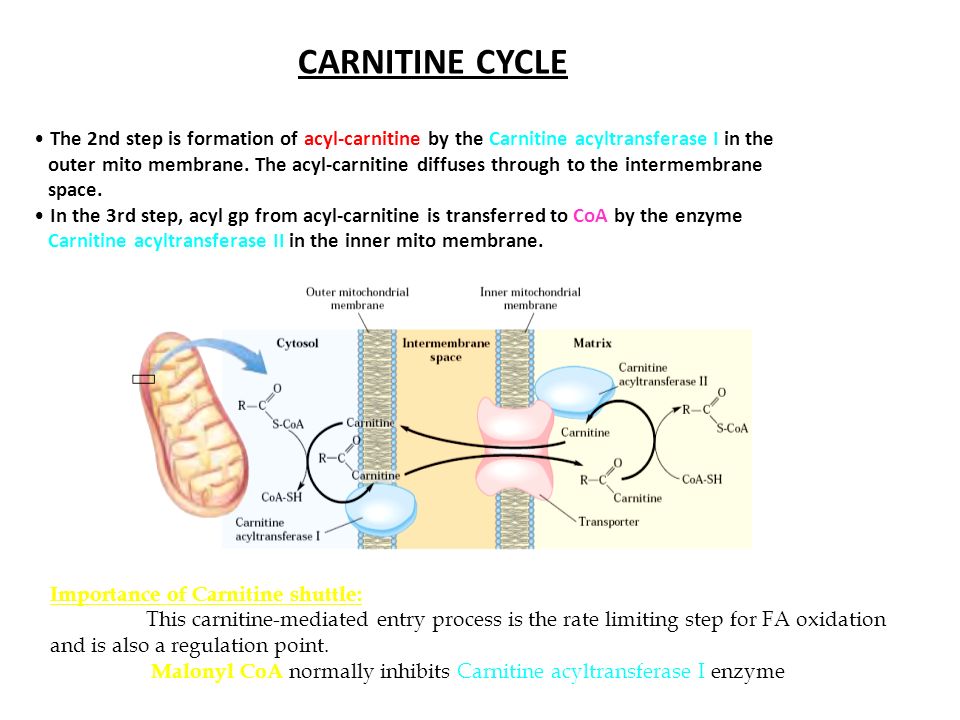
Lesson on the carnitine shuttle. This carnitine shuttle is a rate limiting step in the oxidation of fatty acids in the mitochondria and thus fatty acid oxidation can be regulated at this step.

Carnitine Shuttle Purpose And Mechanism
Role Of Carnitine In Disease Nutrition Metabolism Full Text
Fatty Acid Oxidation Occurs Inside Mitochondria Ppt Video Online
Carnitine then diffuses back across the membrane by carnitine acylcarnitine translocase into the mitochondrial intermembrane space.
Carnitine shuttle. This enzyme brings fatty acyl carnitine into the matrix and carnitine back into the intermembrane space to get and combine with the next fatty acyl coa in the intermembrane space. Once carnitine is released the long chain acyl coa derivative enters the beta oxidation pathway. Carnitine shuttle fatty acid oxidation.
Ketone body formation and utilization. Malonyl coa an intermediate of fatty acid synthesis present in the cytosol is an inhibitor of carnitine acyltransferase i. Cpt2 is carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2.
Primary carnitine deficiency or carnitine transporter defect is an autosomal recessive disorder of fatty acid oxidation caused by heterozygous mutations in the slc22a5 gene that encodes the high affinity carnitine transporter octn2. Metabolic cardiomyopathy is the hallmark symptom of this disease. Fatty acids are oxidized in mitochondria and synthesized in the cytoplasm.
The flux generating step in kb formation is usually. Regulation of carnitine shuttle. This disorder prevents the shuttle like action of carnitine from assisting fatty acids across the mitochondrial membrane and therefore there is decreased fatty acid catabolism.
A disorder is associated with carnitine acylcarnitine translocase deficiency. Carnitine acyl carnitine translocase. The mobilization of alternative substrates for gluconeogenesis.
Carnitine is an important metabolite derived from our diet or biosynthesized from lysine and methionine. This is called the carnitine shuttle system. The carnitine shuttle is responsible for transferring long chain fatty acids across the barrier of the inner mitochondrial membrane to gain access to the enzymes of beta oxidation.
This enzyme replaces carnitine with coa. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Activation and transportation of fatty acids into the mitochondria the free floating fatty acids released from adipose tissues to the blood bind to carrier protein molecule known as serum albumin that carry the fatty acids to the cytoplasm of target cells such as the heart skeletal muscle and other tissue cells where they are used for fuel.
Start studying lecture 21 carnitine shuttle and beta oxidation of fatty acids. With every complete cycle a two carbon fragment is cleaved and an acetyl coa molecule is released.

Carnitine Shuttle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Elevated Acylcarnitine Compounds And Associated Hypoglycemia

Fatty Acid Entry Into Mitochondria Glucose Phosphate

EmoticonEmoticon